Glossary of activated carbon
Glossary Table of Contents
Activated carbon structure
Activated carbon is based as carbon to form the main components. After activation, the structure of ativated carbon is made from graphite-like crystallites and hydrocarbon. It is unlike the complex macromolecular structure of carbides, but a random or amorphous structure.
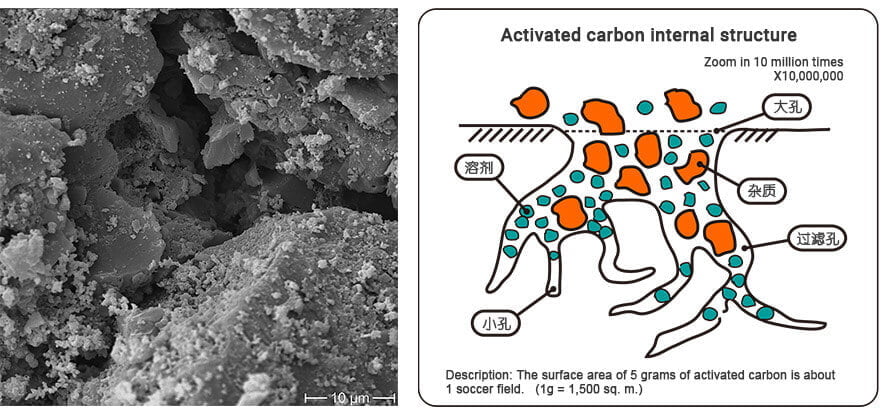
Active carbon adsorption
With activation and carbonization, activated carbon will form the large surface area, which makes it as the ideal adsoprtion material in our life. So it is effective to remove the unwated taste, odour and micropollutants in the water and air treatment.
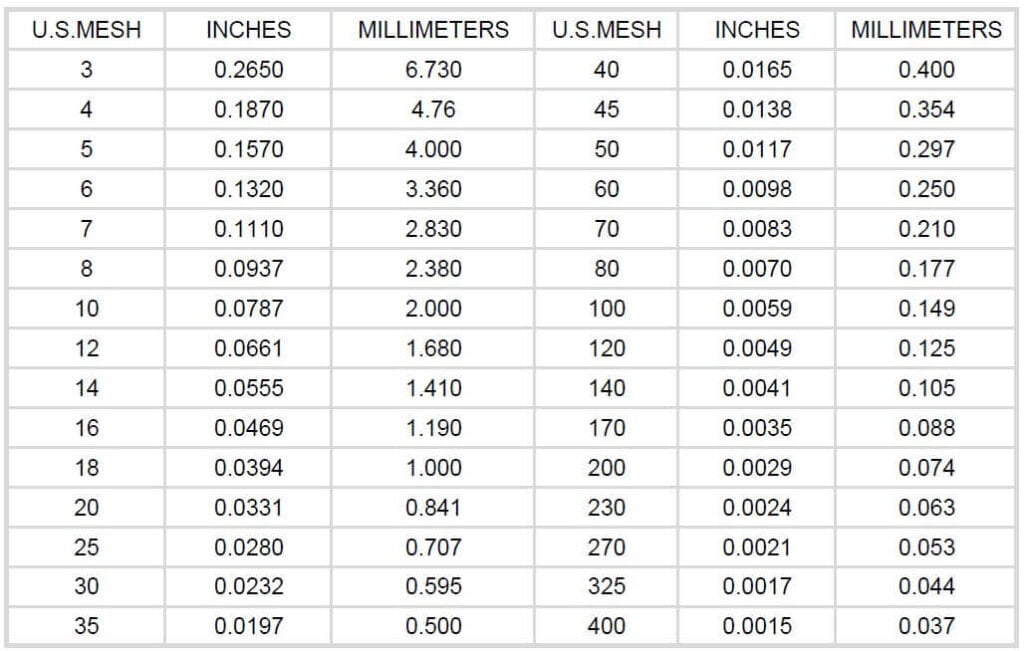
Activated carbon mesh size (ASTM D2862-10)
According to different mesh size, the activated carbon also can be devided into pellet, powder and granular activated carbon. In the specific application, clients can choose the most suitable activated carbon as the best solutions.
Density of activated carbon
The density of activated carbon is generally apparent density, sometimes called bulk density. It is the weight of activated carbon per unit volume.
The following is the bulk density of activated carbon:
- Granular activated carbon: 0.45-0.65g/cm3
- Powder activated carbon: 0.38-0.45g/cm3
- Coconut shell and coal activated carbon: 0.5-0.55g/cm3
Bulk density is very important for loading container.
Activated carbon pore size distribution
Because of the different raw material and production process, activated carbon pore size varies. It has three types: macroporous, mesoporous and microporous.
- Macroporous: >50nm
- Mesoporous: 2-50nm
- Microporous: <2nm
Activated carbon iodine value (ASTM D4607-94)
Iodine value is also the iodine absorption value, which is used to indicate the absorption capacity of activated carbon for liquid substances;
It is the most important index of activated carbon. The higher the iodine is, the better activated carbon is.
Moisture content
After activation and carbonization, the moisture of activated carbon is very less. The following is the moisture of different activated carbon types.
- Coconut shell activated carbon: <5%
- Coal activated carbon: <5%
- Wood powder activated caron: 10-12%
Generally, the moisture of activated carbon is very easy to determine by oven drying method.
Ash (ASTM D2866-94)
In addition to carbon, the chemical composition of activated carbon also contains two substances, one is chemically bonded elements, such as oxygen and hydrogen; the other is ash.
The ash content varies with the different types of activated carbon. And the relative content of ash in activated carbon increases with the degree of carbon activation of the raw material.
- Coconut shell activated carbon: <3%
- Coal based activated carbon: 8-15%
Generally,for water and air filters application, we need to control the ash of activated carbon, so that it will affect the machine working performance.
Activated carbon hardness (ASTM D3802-89)
Hardness refers to the wear resistance of activated carbon. They have a great relationship.
These mechanical properties directly affect the performance of activated carbon. For example, in the gold recovery, choosing the better hardness of activated carbon is particularly important, which will reduce gold loss with high carbonaceous hardness.
Methylene blue value
The methylene blue value is used to represent the decolorization ability of activated carbon. It is mostly used to indicate the liquid decolorization ability of powdered activated carbon. The higher the methylene blue value is, the better the decolorization performance will be under the same unit weight.
The detection of methylene blue by coal-based activated carbon is usually in mg/g, and ml/0.1g is used for wood-based activated carbon.
Molasses value
Refers to the decolorization ability of activated carbon on molasses solution. The molasses value is also a sign of development degree of the macropores of activated carbon. There is no detection standard for molasses value in China. Generally, the standard of Calgon in the United States is used for testing.
In China, through coal blending technology to adjust the pore distribution, it can also produce large pores of activated carbon, which is called agglomerated activated carbons. With the high molasses value, it can be used in macromolecules fields.
CTC (ASTM D3476-04)
carbon tetrachloride (CTC) adsorption value is used to indicate the absorption capacity of activated carbon for gas substances. It is the main detection method for the quality control of gas-phase.
Activated carbon regeneration
Activated carbon has been as the common adsorben in the word. How to deal with the used activated carbon has become an important problem. When activated carbon reaches a saturation point after a period of adsorption, and most of the activated carbon is directly discarded, buried or incinerated. This has caused a waste of resources and environmental pollution. In fact, used activated carbon can be regenerated..
Activated carbon regeneration is to reactivate the fully adsorbed activated carbon after being treated under certain conditions. Activated carbon adsorption is a physical process, so high-temperature can desorbe the impuries inside to restore their original activity.